Operate Value Stream
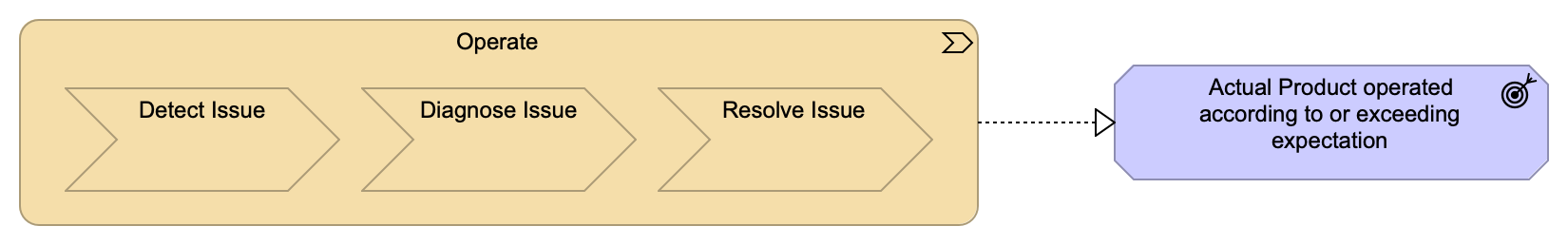
Overview
The value stream “Operate”, as shown in Operate Value Stream Model, monitors and ensures that the availability and performance of Actual Product Instances are within the boundaries of their agreed Service Contract and Key Performance Indicator (KPI) targets. The scope of this value stream includes managing any compliance and security aspects of running Digital Product Instances and underlying systems that may result from deployment and/or fulfillment. The IT4IT Standard describes how to achieve this using integrated, automated, or fully autonomous data flows between the event monitoring (Event, Incident, Change, Configuration, and Problem Management) functions of the digital services. In addition, the data flows may be designed to be reactive, proactive, or predictive, and include a retrospective.
The Operate value stream delivering the Actual Product Instance is operated in a sustainable way within the agreed terms and conditions of a Service Contract.
Primary Stakeholder
The primary stakeholder of the Operate value stream is the Consumer, who can use an Actual Product Instance or system within the boundaries of the Service Contract.
Value
The outcome of the Operate value stream is to ensure that the Actual Product Instance operates, and can be consumed as agreed in the terms of the Service Contract.
Cross-Value Stream Dependencies
The Operate value stream depends on:
-
Deploy:
-
Actual Product Instances can be enabled, changed, or disabled by the deployment of the Product Release
-
-
Consume:
-
Actual Product Instances can be enabled, changed, or disabled by the fulfillment of the Service Offer
-
Consumption of a Service Offer can result in an Incident that needs to be handled in the Operate value stream
-
Value streams that depend on the Operate value stream are:
-
Evaluate:
-
Improvements start with drivers that are expected to arise from all seven value streams
All value streams will capture data to ensure the quality of the Digital Product will meet the requirements. Quality is an aspect of each task within each value stream. The Evaluate value stream uses data produced in all value streams to evaluate drivers.
-
-
Integrate:
-
Problems related to Actual Product Instances can require a fix from development (system defect)
-
-
Consume:
-
Fulfillment feedback of a Service Offer that resulted in an Incident and needed to be handled in the Operate value stream
-
The Operate value stream, as shown in Operate Value Stream Details Model, is the more comprehensive view for included scenarios and detailed value stream stages for the value stream, and will be described in detail in the following sections.
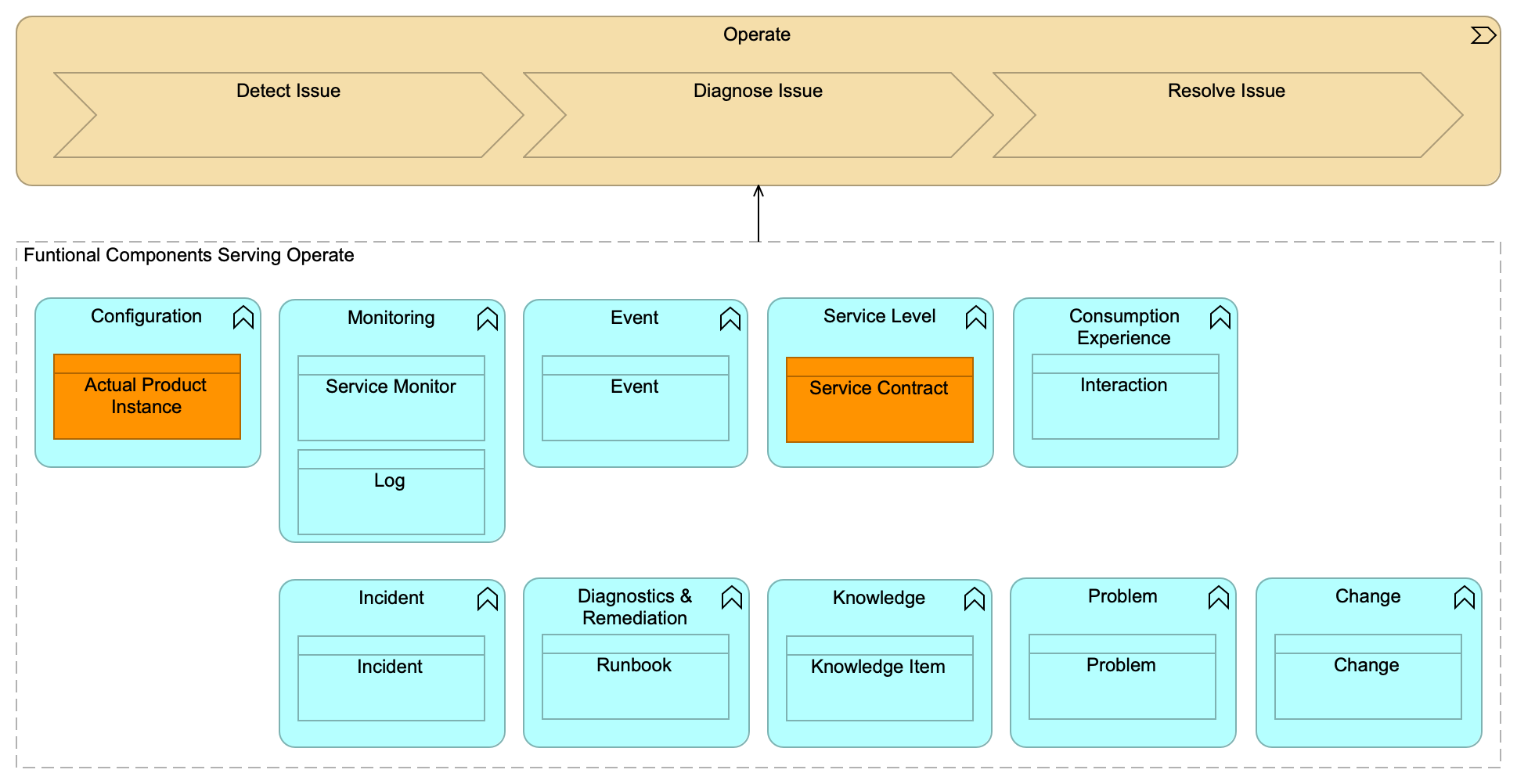
In the following sections we document the scenarios and stages of the Operate value stream:
-
Scenario: Remediate an Identified Back-End Issue
-
Scenario: Ensure Disaster Recovery Objectives
-
Scenario: Remediate a major Event or Incident
-
Scenario: Remediate Consumer Front-End Issue
-
Scenario: Perform Scheduled Maintenance
-
Stage: Detect Issue
-
Stage: Diagnose Issue
-
Stage: Resolve Issue
Operate Scenarios
The Operate value stream is applicable for the following five scenarios:
Remediate an Identified Back-End Issue Scenario
In this scenario, the Operate value stream is triggered by an issue (a breach and/or vulnerability) or a potential future issue (triggered by a threshold breach) in the infrastructure, platforms, applications, user transactions, and/or behavior of the back-end network. The scenario ends with the outcome that the service remains operational without affecting consumer experience and within the boundaries of the Service Contract.
The activities undertaken in the scenario include the detection, diagnosis, evaluation, and resolution of issues, alerts, and anomalies related to the performance, compliance, and security aspects of the organization’s back-end.
-
Performance remediation examples include: “reactive” event detection and correlation through the monitoring of the Digital Product Instance, system, and topology; “pro-active” event detection through test transactions or built-in self-healing capabilities; or “predictive” event detection, done by generating test events from the analysis of historical monitoring data and other data sources (e.g., business performance, social media, weather) to identify potential degradation based on predicted consumer behavior
-
Security remediation examples include responses to different types of attack, including unauthorized system access, phishing, password cracking, spyware, malware, Denial of Service (DoS) attacks, and more
-
Compliance remediation examples include inspections to detect compliance with the rules; for example, adherence to legislation, statutes, regulations, standards, policies, contracts, processes, procedures, and operational controls
Ensure Disaster Recovery Objectives Scenario
This scenario is about ensuring that any capabilities listed in the business continuity/disaster recovery plan can work within the boundaries of the Service Contract. The activities in this scenario, which are planned and triggered by the business continuity and/or disaster recovery plan activities calendar, include: detection, diagnosis, and remediation tasks related to the plan. The purpose of the activities is to ensure that recovery objectives (e.g., Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO), Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO)) remain within the boundaries of the agreed Service Contract and BIA. Real-world examples of these activities include performing backups, ensuring plans and mechanisms for graceful degradation, removing Single Points Of Failure (SPOFs), validating recovery libraries, performing redundancy validations, testing backup sites, and performing running (scheduled or random) disaster recovery simulations.
Remediate a Major Event or Incident Scenario
This scenario is triggered by a major event (e.g., full system outage, significant application failure); its outcome is that the service is restored within the boundaries of the Service Contract. The activities undertaken in the scenario include the correlation of Events/Incidents to identify (detect) that a major Event/Incident has occurred, collaboration with multiple teams to perform research and analysis to determine the underlying cause of the issue and to establish a remediation plan (diagnose), and the execution of remediation plans by those involved to resolve the major Event/Incident and restore services.
Remediate Consumer Front-End Issue Scenario
This scenario is triggered when an issue is raised by or through the service desk. The outcome of the scenario is restored consumer experience, normal service operations, and service delivery to the consumer within the boundaries of the Service Contract. The activities of the scenario include capturing/detecting, diagnosing, resolving, and evaluating any service interactions raised and escalated by consumers or the service desk. This might include service interactions which have been generated by users or by the service desk, and have been subsequently escalated into an Incident, requiring second or third-line handling for remediation. In cases where handling is not or cannot be performed due to operational decisions or lack of capacity, the risk of working outside of agreed boundaries will be logged and communicated with the consumer and can be input into the Evaluate value stream.
Perform Scheduled Maintenance Scenario
This scenario is triggered when a planned activity is scheduled or when certain thresholds are met which trigger an alert/event for proactive maintenance. The planned activity or maintenance is reviewed and scheduled. Manual or automated action is taken to complete the activity/maintenance.
Detect Issue Stage
Description
The purpose of the value stream stage “Detect Issue” is to detect issues in an Actual Product Instance or system that has caused or may cause degradation of the service or breach the agreed service levels, then to prioritize and assign them for further diagnosis in a structured and repeatable manner.
Entrance Criteria:
|
Exit Criteria:
|
Value Item:
|
|
Activities:
|
|
Examples of Participating Stakeholders:
|
Participating Data Objects (Component): |
Diagnose Issue Stage
Description
The purpose of the value stream stage “Diagnose Issue” is to prepare the best/quickest course of action to retain or restore normal operations. Further diagnosis can be performed to identify the root cause(s) of a potential or detected issue.
Entrance Criteria:
|
Exit Criteria:
|
Value Item:
|
|
Activities:
|
|
Examples of Participating Stakeholders:
|
Participating Data Objects (Component): |
Resolve Issue Stage
Description
The purpose of the value stream stage “Resolve Issue” is to execute the (prepared) course of action to retain, restore, and confirm normal service operations.
Entrance Criteria:
|
Exit Criteria:
|
Value Item:
|
|
Activities:
|
|
Examples of Participating Stakeholders:
|
Participating Data Objects (Component): |