Information Management Topics
Description
Social, Mobile, Analytics, and Cloud
Discussions of Digital Transformation often reference the algorithm SMAC:
-
Social
-
Mobile
-
Analytics
-
Cloud computing
Others would add IoT. These are not equivalent terms; in fact, they have relationships to each other; see Social, Mobile, Analytics, and Cloud.
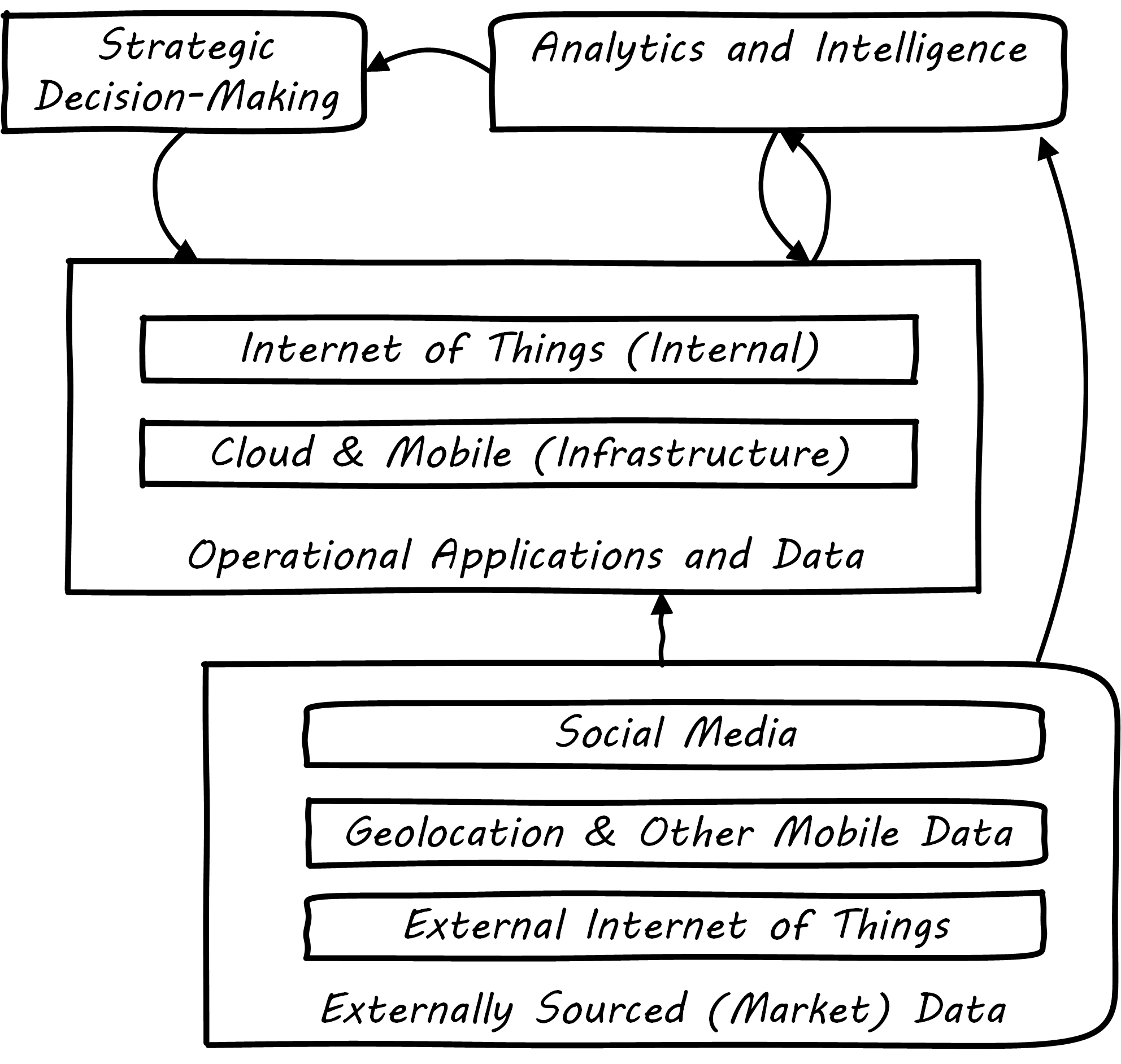
Social media is generally external to an organization and manifests as a form of commercial data, that provides essential insights into bow a company’s products are performing and being received.
Mobile (or mobility) has two distinct aspects: mobility as an engagement platform (e.g., for deployment of “apps” as one product form), versus the commercial data available from mobile carriers, notably geolocation data.
IoT can be either an internal or external data source, often extremely high volume and velocity, requiring analysis services for sense-making and value extraction.
Big Data
The term “Big Data” in general refers to data that exceeds the traditional data management and data warehousing approaches we have discussed above.
As proposed by analyst Doug Laney in 2001 [Laney 2001], its most well-known definition identifies three dimensions of scale:
-
Volume
-
Variety
-
Velocity
For example, high-volume data is seen in the search history logs of search engines such as Google.
High-variety data encompasses rich media and unstructured data, such as social media interactions.
High-velocity data includes telemetry from IoT devices or other sources capable of emitting large volumes of data very quickly.
All of these dimensions require increasingly specialized techniques as they scale, and the data management product ecosystem has continued to diversify as a result.
Managing the Information of Digital Delivery
| We have talked about metadata previously, and understanding business impact with the CMDB. You should review that material before continuing. |
Regarding our previous data warehousing architecture, the digital pipeline can be seen as related to four areas; see The Data Architecture of Digital Management:
-
Product management
-
IT
-
Support
-
Operations
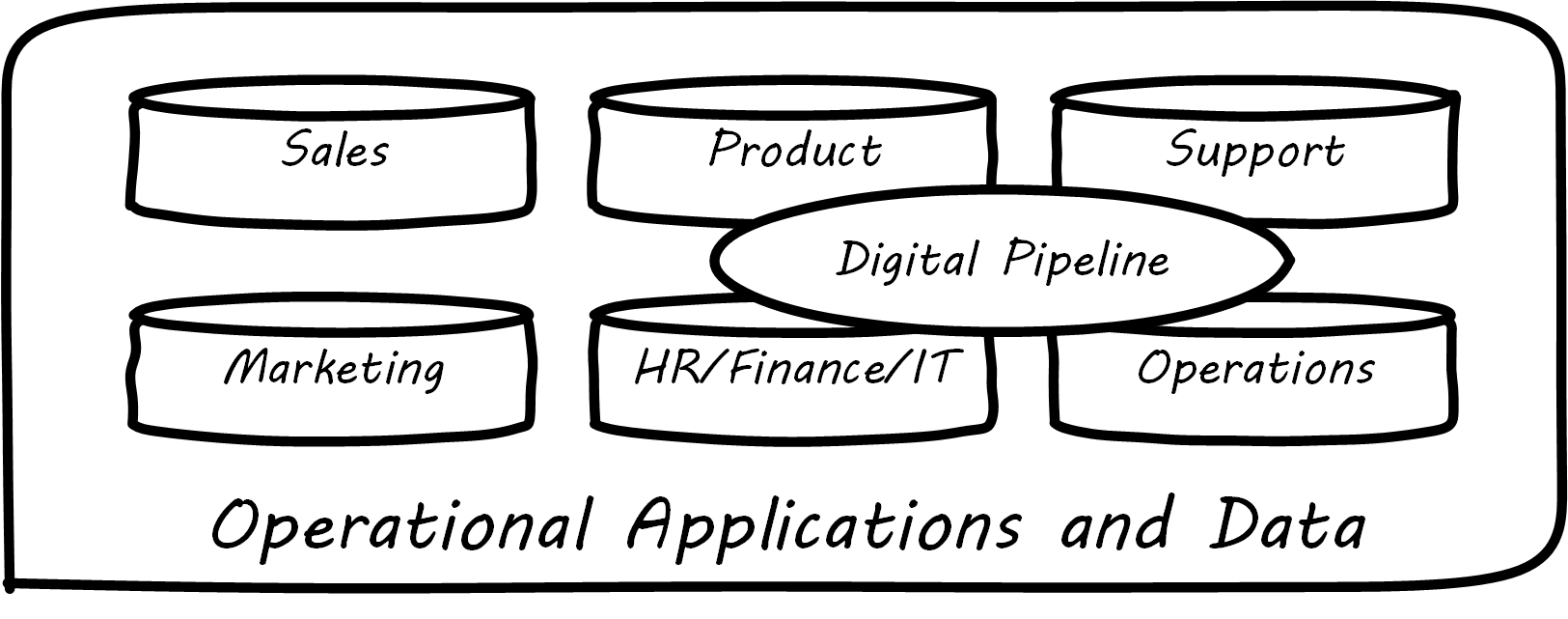
Assume the primary product of the organization is an information-centric digital service, based ultimately on data. How do you manage data? How do you manage anything? In part, through collecting data about it. Wait – “data about data”? There’s a word for that: metadata. We will take some time examining it, and its broader relationships to the digital delivery pipeline. The association of business definitions with particular data structures is one form of metadata. Data governance, records management, and ongoing support for digital consumers all require some layer of interpretation and context to enrich the raw data resource.
Consider the list shown in Servers and Databases.
| Server | Database |
|---|---|
SRV001 |
DB0023 |
SRV001 |
DB0045 |
SRV002 |
DB0067 |
Not very useful, is it? Compare it to Servers, Databases, Product, and Governance Information.
| Server | Database | Product | Regulatory |
|---|---|---|---|
SRV001 |
DB0023 |
Online reviews |
Customer privacy |
SRV001 |
DB0045 |
Employee records management |
HIPAA, PII |
SRV002 |
DB0067 |
Online sales |
PCI, PII |
We could also include definitions of the tables and columns held in each of those databases. However, what system would contain such data? There have been a couple of primary answers over the years: metadata repositories and CMDBs.
In terms of this document’s general definition of metadata as non-runtime information related to digital assets, both the metadata repository and the CMDB contain metadata. However, they are not the only systems in which data related to digital services is seen. Other systems include monitoring systems, portfolio management systems, risk and policy management systems, and much more. All of these systems themselves can be aggregated into a data warehousing/BI closed-loop infrastructure.
This means that the digital organization, including organizations transforming from older IT-centric models, can apply Big Data, machine learning, text analytics, and the rest of the techniques and practices covered in this Competency Category.
| We will examine a full “business of IT/digital delivery pipeline” architecture in the next Competency Category. |
Evidence of Notability
Considered in each specific topic area.
Limitations
Considered in each specific topic area.
Competency Category "Topics in Information Management" Example Competencies
-
Identify the themes of social, mobile, analytics, and cloud as modern digital channels and platforms
-
Identify the data management concerns of the digital pipeline itself
Related Topics